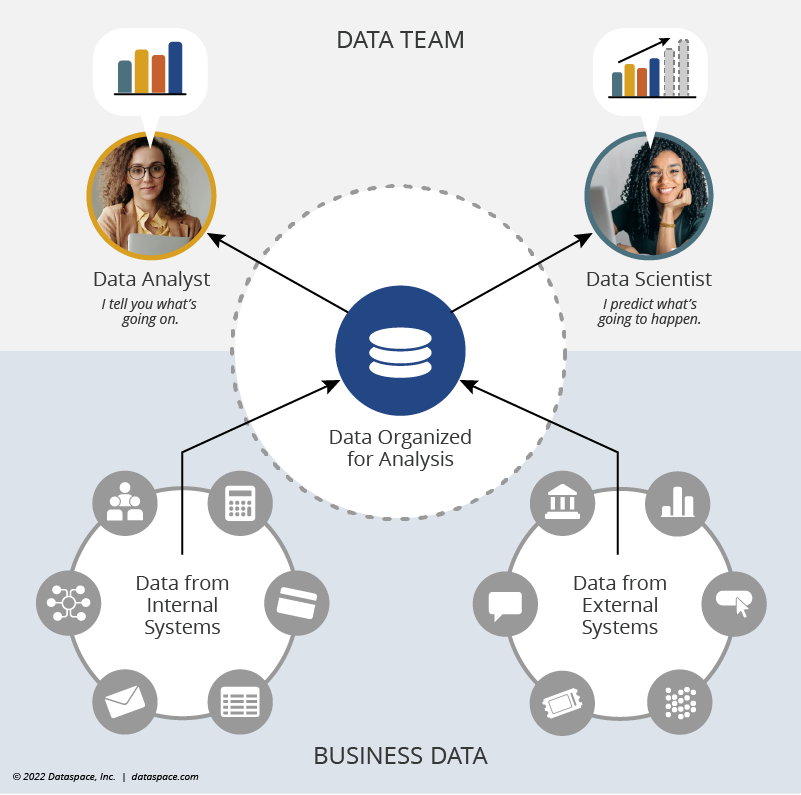
We’ve been exploring the three major areas of data and analytics roles common to the modern data team. In our last post, we took a deep dive into the different types of data analysts out there—all tasked with describing the current state of a business.
Similar to data analysts, data scientists collect and analyze business data, but they take it a step further. Data scientists use advanced statistical models, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to predict the likelihood of future business outcomes. In our earlier post, we gave the following comparison:
The data analyst tells you who responded to particular promotions. The data scientist tells you the likely effect of changes to those promotions.
When you consider the magnitude of data created every day—much of it as a result of doing business—it’s no surprise that data scientist is the highest growth field in data and analytics, with a five-year job growth rate of 480%!
Why data scientist roles are vital to business success
On the surface, data science can feel a bit like voodoo. While their value to business is clear what’s unclear is what it is they actually do to create that value. The key thing to remember here is the “science” part. Unlike the analyst, who uses a straightforward and set process to make sense of business data, the way a data scientist interacts with data is more like an experiment. A data scientist will:
- Investigate a business problem and form a hypothesis.
- Write and deploy algorithms to test that hypothesis.
- Identify, gather, organize, and clean the required data.
- Run and assess the results of their code and interpret meaning.
- Revise algorithms and repeat until they can produce consistent, reliable insights from their work.
The goal here is to create a unique system, designed around a particular business, that can reliably create value, either as part of a product or service offering (eg: Google search, video games, virtual personal assistants, Amazon product recommendations) or as part of business management (eg: understanding customer behavior, planning product development, projecting profit and loss).
Not only will the data scientist build these systems, they will also maintain them. This involves reassessing, updating and improving their methodologies as new and better data sources become available.
A data scientist is a data scientist is a data scientist
While data scientists are highly specialized roles, often requiring a PhD, data scientist job titles tend to be rather generic. Perhaps it’s because of the swiss-army-knife of skills they must possess, or simply because it’s a comparatively newer field. For whatever reason, a data scientist is often simply called a Data Scientist. Some notable exceptions are titles that include the following specializations (though not always):
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is the complex process of recreating human-level intelligence through computers. AI has become the cornerstone of modern technological advancement. As a result, data scientists focused in AI are in especially high demand. Job titles such as AI Engineer or AI Research Scientists are common examples of data scientists roles.
Machine Learning (ML)
ML is a subset of AI that is centered on designing and applying computational algorithms to mimic the way humans learn. Job titles like ML Engineer, ML Scientist, are common to data scientist roles focused on the discipline.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Another branch of AI, NLP is focused on creating systems that can understand human language, as it is written or spoken. Job titles for data scientists specializing in NLP can include, NLP Analyst, NLP Scientist, and NLP Engineer.
Operations Research (OR)
OR is an area of data science that is particularly relevant to business management. Data scientists with Job titles such as Operations Research Specialist, or Operations Research Scientist, will be focused on creating systems to help with business decision making.
Statistics
A deep understanding of statistics is absolutely core to data science. It is the methodology that drives the algorithms used throughout the field. Yet there are some data scientist roles that are laser-focused on statistical methods. These may include titles like Statistician, Statistical Scientist, or Statistical Engineer.
As the field of data science evolves and matures, many expect to see more diversity and specificity in data scientist job titles. Data Scientist will likely cease to be a career much in the same way Computer Scientist is not usually used as a job title. But the field of data science will be vast and support a wide range of career paths.
Things to consider when hiring a data scientist
If your business is ready for the type of insights only a data scientist can provide, you’ll want to keep these things in mind during the hiring process:
Demand for Data Scientists
As we wrote above, data scientists are in extraordinarily high demand. If you have an open data scientist role to fill, be prepared for a long search process. Because of the advanced level of education required—often a PhD—the talent pool is already relatively small. When you consider off-the-charts job growth, there simply aren’t enough experienced data scientists to go around. As with other high-demand data jobs, highly-qualified data scientists are being proactively contacted by professional recruiters for roles that never make it to a job board.
Data Scientist Pay
According to Indeed, the average salary for a data scientist in 2021 was just over $122,000 per year. Given recent demand, at Dataspace, we rarely see data scientist roles with salaries less than $150k. And many roles are filled at closer to $200k per year. When you consider the level of education required and the shortage of talent, it’s no surprise that experienced data scientists are commanding premium salaries.
Role of Data Scientists
Data science has broad application across business functions, from operations to offerings. If your business could be doing things better, from building a better product line to running business more efficiently, there’s not a lot of question if a data scientist could help drive business success. The determining factor will more likely be whether you have the infrastructure and team to support the role. Data scientists are usually part of a mature data team and frequently require the support of data engineers and analysts to provide value.
Common Data Science Skills
There’s a reason data scientists are called “unicorns.” They must possess a diverse and ever-evolving skillset. They are required to be masters at highly-technical fields, such as statistics, analytics, and programming, but also have a deep understanding of business and an exceptional ability to communicate. Additionally, they may have highly-specialized expertise in disciplines such as AI, ML, or NLP, among others. Of course your needs will depend on the purpose of the role within your organization as well as your industry.
Assessing the skills of a data scientist is particularly challenging for non-technical hiring managers, yet it’s a critical step in the hiring process. With such esoteric knowledge, it’s helpful to have expert assistance assessing candidates if you don’t already have a senior data scientist on your team.
Data Science Experience
Typically, a career as a data scientist requires an advanced degree on top of technically-focused undergraduate studies. But the skills are so broadly applicable that actual jobs can vary greatly from business to business. As a result, we find most organizations prefer to hire a data scientist with experience in their industry. However, this can make a difficult search nearly impossible. An expert data scientist will be exceptionally adaptable and a strong critical thinker. They should be well versed in evolving their thinking and their approach to meet the needs of each unique situation. We often encourage our clients to not weigh industry experience too heavily when considering an otherwise exceptional candidate.
Data scientists will soon be indispensable to business
Does every business need a data scientist? No, not right now. But any business that is driven by data should be investing in data science, if they aren’t already. Analytics has traditionally operated in the realm of business management. But data science is evolving to guide every aspect of business, including product/service development and operations. If your business is positioning itself for major success within the next decade, it’s important to put data scientist roles in your growth plan today.
Do you need assistance evaluating if a data science role would be valuable to your business?
Are you having a hard time finding an experienced data scientist with the skills you need? Contact our expert data science recruiters to learn more about how we can help.

